Ongoing ClickFix Campaign
10 July 2025
There have been reports of threat actors using a social engineering technique known as ClickFix to trick potential victims into executing malicious commands.
Background
There have been reports of threat actors using a social engineering technique known as ClickFix to trick potential victims into executing malicious commands under the pretense of providing “quick fixes” for common computer issues. ClickFix has reportedly targeted organisations across a broad range of sectors, including the technology, financial services, manufacturing, wholesale and retail, government, professional and legal services, utilities and energy. This current campaign is targeting the hospitality sector.
What is ClickFix?
ClickFix is a relatively new social engineering technique increasingly used by threat actors in their campaign. This technique misleads targeted users into applying supposed “quick fixes” for common computer issues, such as performance issues, missing drivers or pop-up errors. Since it's initial reports in 2024, ClickFix has resulted in multiple malware distribution campaigns involving compromised websites, malicious distribution infrastructure and e-mail phishing.
Tactics, Techniques and Procedures (TTPs)
The ClickFix technique relies on clipboard hijacking, where malicious software secretly intercepts and modifies information that victims copy and paste on their devices. It typically uses dialogue boxes or a fake Blue Screen of Death (BSoD) containing fake error messages to trick victims into copying malicious script or commands on their own clipboards using ClickFix inject before providing instructions to paste and run the malicious content. In recent months, threat actors have also been observed to use phishing emails redirecting victims to their intended webpage. After completing a CAPTCHA challenge, a fake Blue Screen of Death (BSoD) pops up with instructions for the victim. An example of a ClickFix campaign pop-up message is shown in Annex A and B.
The victims typically follow a three-step process that enables the execution of malicious PowerShell commands:
Open a Windows Run dialog box
Automatically or manually copy and paste a malicious PowerShell command into the terminal [press 'CTRL+V']
And run the prompt [press ‘Enter’]
Because the ClickFix technique relies on users pasting the content, this is sometimes referred to as “pastejacking.” Threat actors often use the ClickFix technique as an initial infection vector to deploy malicious payloads such as infostealers, remote access trojans (RATs) or disable existing security tools.
This delivery method bypasses many standard detection and prevention controls, as the attack does not depend on any exploit, attachment or malicious link. Instead, potential victims unknowingly run the malicious command themselves, through a trusted system shell. This method makes infections from ClickFix more difficult to detect than drive-by downloads or traditional malware droppers.
Impact
Successful execution of the ClickFix technique can lead to the deployment of various malware families, including the DCRAT, NetSupport RAT, Latrodectus, and Lumma Stealer, resulting in credential theft, data exfiltration, email account compromise, and potential ransomware incidents. Threat actors can utilise their access to compromised systems to drop secondary payloads, perform privilege escalation and move laterally across other systems within the network.
How to Protect Your Organisations
Organisations are advised to adopt the following mitigation measures to safeguard against the ClickFix Campaign:
Remain vigilant against fake “CAPTCHA” or “Fix It” prompts and recognise the tell-tale signs (e.g. unexpected run-dialog instructions or unofficial BSoDs) of the ClickFix campaign.
Remain vigilant against other attack vectors that could be chained to redirect users to the ClickFix site (eg: phishing emails)
Update your systems, applications and software to the latest versions and use an up-to-date anti-virus software to detect malware and malicious phishing links.
Implement Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions to perform logging, asset visibility, and continuous system monitoring to detect anomalous network connections and malicious PowerShell commands.
Enforce strict access control policies, ensuring users and systems only have the minimum permissions necessary. This limits the impact of a successful compromise by preventing privilege escalation and lateral movement.
Implement application whitelisting to allow only approved software and scripts to execute, effectively blocking unknown executables and malicious PowerShell scripts typically used in ClickFix campaigns.
Administrators may wish to consider tracking and blocking the Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) associated with the ClickFix campaign. Possible IOCs associated with the ClickFix campaign are shown in the table below:
Indicators of Compromise (Phishing URL)
Malware Variant | URL |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]headkickscountry[.]com/lz1y |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]activatecapagm[.]com/j8r3 |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]homelycareinc[.]com/po7r |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]byliljedahl[.]com/8anf |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]byliljedahl[.]com/8anf |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]jamerimprovementsllc[.]com/ao9o |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]seedsuccesspath[.]com/6m8a |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]zenavuurwerkofficial[.]com/62is |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]brownsugarcheesecakebar[.]com/ajm4 |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]hareandhosta[.]com/95xh |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]zenavuurwerkofficial[.]com/62is |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]customvanityco[.]com/izsb |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]byliljedahl[.]com/lv6q |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]confirmation887-booking[.]com/17149438 |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]verifyguest02667-booking[.]com/17149438 |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]guest03442-booking[.]com/17149438 |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]confirmation8324-booking[.]com/17149438 |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]cardverify0006-booking[.]com/37858999 |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]verifycard45625-expedia[.]com/67764524 |
Indicators of Compromise (SHA256)
Malware Variant | SHA256 | File Name |
Lumma Stealer | 2bc23b53bb76e59d84b0175e8cba68695a21ed74be9327f0b6ba37edc2daaeef | PartyContinued.exe |
Lumma Stealer | 06efe89da25a627493ef383f1be58c95c3c89a20ebb4af4696d82e729c75d1a7 | Boat.pst |
Latrodectus | 5809c889e7507d357e64ea15c7d7b22005dbf246aefdd3329d4a5c58d482e7e1 | libecf.dll |
Latrodectus | 52e6e819720fede0d12dcc5430ff15f70b5656cbd3d5d251abfc2dcd22783293 | PowerShell Downloader |
Latrodectus | 57e75c98b22d1453da5b2642c8daf6c363c60552e77a52ad154c200187d20b9a | JavaScript Downloader |
Latrodectus | 33a0cf0a0105d8b65cf62f31ec0a6dcd48e781d1fece35b963c6267ab2875559 | JavaScript Downloader |
NetSupport RAT | 5C762FF1F604E92ECD9FD1DC5D1CB24B3AF4B4E0D25DE462C78F7AC0F897FC2D | data_3.bin |
NetSupport RAT | 9DCA5241822A0E954484D6C303475F94978B6EF0A016CBAE1FBA29D0AED86288 | data_4.bin |
NetSupport RAT | CBAF513E7FD4322B14ADCC34B34D793D79076AD310925981548E8D3CFF886527 | msvcp140.dll |
NetSupport RAT | 506ab08d0a71610793ae2a5c4c26b1eb35fd9e3c8749cd63877b03c205feb48a | libsqlite3-0.dll |
DCRAT | cd3604fb9fe210261de11921ff1bea0a7bf948ad477d063e17863cede1fadc41 | Ps1.ps1 |
DCRAT | 13b25ae54f3a28f6d01be29bee045e1842b1ebb6fd8d6aca23783791a461d9dd | payload_1.ps1 |
DCRAT | 9fac0304cfa56ca5232f61034a796d99b921ba8405166743a5d1b447a7389e4f | .ps1 |
DCRAT | cd3604fb9fe210261de11921ff1bea0a7bf948ad477d063e17863cede1fadc41 | v.proj |
DCRAT | 9fc15d50a3df0ac7fb043e098b890d9201c3bb56a592f168a3a89e7581bc7a7d | v.proj.ps1 |
DCRAT | bf374d8e2a37ff28b4dc9338b45bbf396b8bf088449d05f00aba3c39c54a3731 | Stub.exe/Staxs.exe/tydb7.exe |
DCRAT | 11c1cfce546980287e7d3440033191844b5e5e321052d685f4c9ee49937fa688 | Stub.exe |
DCRAT | 07845fcc83f3b490b9f6b80cb8ebde0be46507395d6cbad8bc57857762f7213a | Stub.exe |
DCRAT | 08037de4a729634fa818ddf03ddd27c28c89f42158af5ede71cf0ae2d78fa198 | Stub.exe |
DCRAT | 2f3d0c15f1c90c5e004377293eaac02d441eb18b59a944b2f2b6201bb36f0d63 | Stub.exe |
DCRAT | 33f0672159bb8f89a809b1628a6cc7dddae7037a288785cff32d9a7b24e86f4b | Stub.exe |
DCRAT | 6bd31dfd36ce82e588f37a9ad233c022e0a87b132dc01b93ebbab05b57e5defd | Stub.exe |
DCRAT | 1f520651958ae1ec9ee788eefe49b9b143630c340dbecd5e9abf56080d2649de | Stub.exe |
DCRAT | 9c891e9dc6fece95b44bb64123f89ddeab7c5efc95bf071fb4457996050f10a0 | DeleteApp.url |
DCRAT | e68a69c93bf149778c4c05a3acb779999bc6d5bcd3d661bfd6656285f928c18e | Wwigu.exe |
DCRAT | 18c75d6f034a1ed389f22883a0007805c7e93af9e43852282aa0c6d5dafaa970 | Wwigu.exe |
DCRAT | 91696f9b909c479be23440a9e4072dd8c11716f2ad3241607b542b202ab831ce | Lbpyjxefa.dll |
Indicators of Compromise (C2)
Malware Variant | C2 Domains |
Lumma Stealer | iplogger[.]co |
Lumma Stealer | stuffgull[.]top |
Lumma Stealer | sumeriavgv[.]digital |
Lumma Stealer | pub-164d8d82c41c4e1b871bc21802a18154.r2[.]dev |
Lumma Stealer | pub-626890a630d8418ea6c2ef0fa17f02ef.r2[.]dev |
Lumma Stealer | pub-164d8d82c41c4e1b871bc21802a18154.r2[.]dev |
Lumma Stealer | pub-a5a2932dc7f143499b865f8580102688.r2[.]dev |
Lumma Stealer | pub-7efc089d5da740a994d1472af48fc689.r2[.]dev |
Lumma Stealer | agroeconb[.]live |
Lumma Stealer | animatcxju[.]live |
Latrodectus | hxxps[:]//webbs[.]live/on/ |
Latrodectus | hxxps[:]//diab[.]live/up/ |
Latrodectus | hxxps[:]//mhbr[.]live/do/ |
Latrodectus | hxxps[:]//decr[.]live/j/ |
Latrodectus | hxxps[:]//lexip[.]live/n/ |
Latrodectus | hxxps[:]//rimz[.]live/u/ |
Latrodectus | hxxps[:]//byjs[.]live/v/ |
Latrodectus | hxxps[:]//btco[.]live/r/ |
Latrodectus | hxxps[:]//izan[.]live/r/ |
Latrodectus | hxxps[:]//k.veuwb[.]live/234 |
Latrodectus | hxxps[:]//r.netluc[.]live |
Latrodectus | heyues[.]live |
Latrodectus | hxxps[:]//k.mailam[.]live/234234 |
NetSupport RAT (Loader) | oktacheck[.]it[.]com |
NetSupport RAT (Loader) | doccsign[.]it[.]com |
NetSupport RAT (Loader) | docusign[.]sa[.]com |
NetSupport RAT (Loader) | dosign[.]it[.]com |
NetSupport RAT (Loader) | loyalcompany[.]net |
NetSupport RAT (Loader) | leocompany[.]org |
NetSupport RAT (Loader) | 80.77.23[.]48 |
NetSupport RAT (Loader) | mhousecreative[.]com |
NetSupport RAT | mh-sns[.]com |
NetSupport RAT | lasix20[.]com |
DCRAT | Oncameraworkout[.]com/ksbo |
DCRAT | low-house[.]com |
DCRAT | http[:]//2fa-bns[.]com |
DCRAT | asj77[.]com |
DCRAT | asj88[.]com |
DCRAT | asj99[.]com |
DCRAT | 194.169.163[.]140 |
DCRAT | 193.221.200[.]233 |
DCRAT | 13.223.25[.]84 |
DCRAT | wmk77[.]com |
DCRAT | 8eh18dhq9wd[.]click |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]ctrlcapaserc[.]com/loggqibkng |
DCRAT | hxxps[://]bqknsieasrs[.]com/loggqibkng |
DCRAT | sqwqwasresbkng[.]com |
DCRAT | 85.208.84[.]94:56001 |
DCRAT | 77.83.207[.]106:56001 |

Annex A: Example of a ClickFix Campaign Pop-up Message
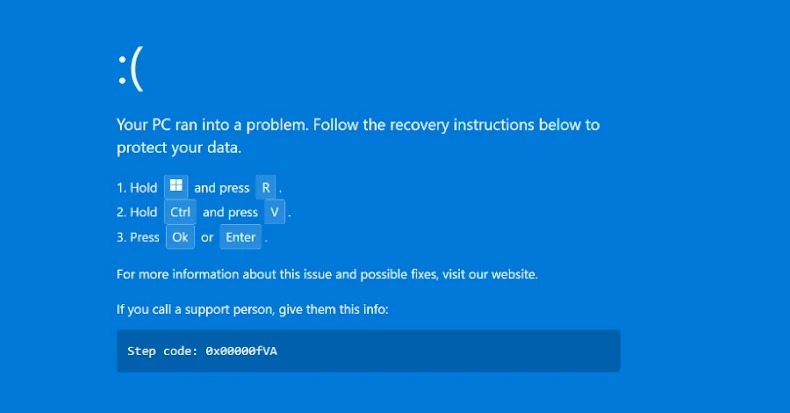
Annex B: Example of ClickFix Fake BSoD Message
More information is available here:
https://www.kaspersky.com/blog/what-is-clickfix/53348/
https://blog.sekoia.io/phishing-campaigns-i-paid-twice-targeting-booking-com-hotels-and-customers/
